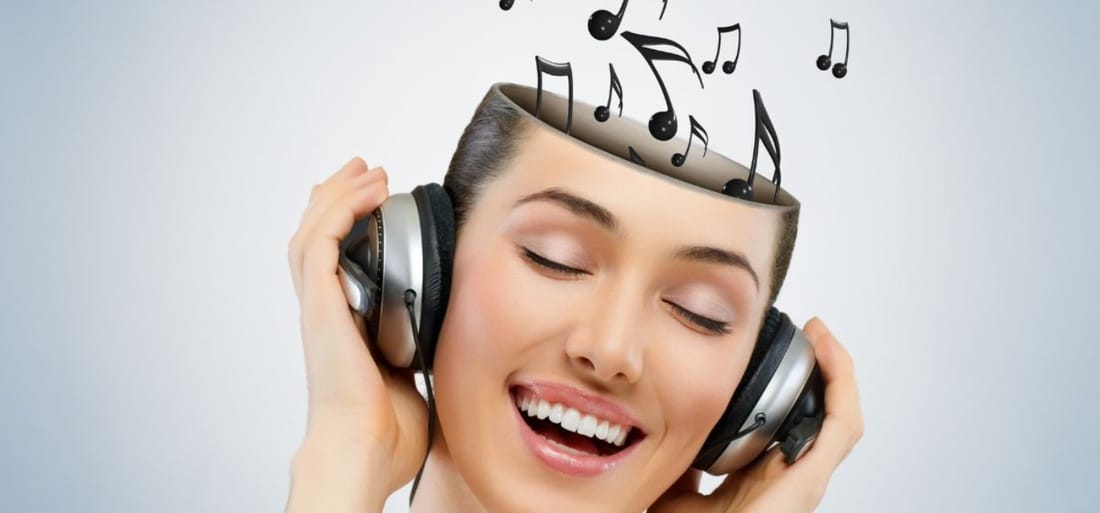
Headphones are more than just a way to listen to music; they’ve become essential tools in our daily lives for entertainment, productivity, and communication. Whether you’re tuning out the world around you or listening to an audiobook during your commute, headphones provide a convenient way to enjoy sound. But what about the side effects they have on the brain? Have you ever thought about how prolonged use affects your mental and auditory health? In this article, we’ll dive into the real side effects of headphones on the brain and provide you with the facts you need to listen wisely.
What are Headphones?
Before exploring their impact, it’s important to understand what headphones are. Essentially, they are devices designed to transmit audio directly to your ears, offering a personal and immersive sound experience. Today, there are several different types of headphones: over-ear, on-ear, and in-ear, each offering unique benefits depending on the situation.
How Headphones Work
Headphones function by converting electrical signals from audio devices into sound waves, which we hear through the ear. Over-ear headphones encircle the ear for a more immersive sound, on-ear models rest lightly on the ears, and in-ear headphones fit snugly inside the ear canal. The sounds you hear depend on the design and the quality of the headphones, with higher-quality devices producing clearer and crisper audio.
Potential Side Effects of Headphones on the Brain
While headphones are a useful tool, they aren’t without their risks. The most immediate concern is their effect on hearing, especially when used at high volumes. Prolonged exposure to loud sound pressure can lead to permanent hearing damage, a condition called noise-induced hearing loss. This can not only affect hearing but could also alter brain activity over time.
Link Between Headphone Usage and Brain Health
The connection between brain health and excessive headphone use isn’t always straightforward. Research suggests that loud music through headphones can alter brain function by overloading the auditory pathways, which may hinder concentration, memory, and cognitive function. The brain, when constantly exposed to high noise levels, has to adapt, and this continuous adjustment can have long-term consequences.
The Role of Sound Frequency and Volume
Not all sound frequencies affect the brain in the same way. Some frequencies might promote relaxation, while others, particularly low-frequency sounds, can induce feelings of anxiety or agitation. The volume level also plays a critical role; sound that’s too loud can lead to overstimulation of the brain, leading to headaches or difficulty concentrating. Limiting exposure to high volume levels and taking regular breaks can significantly minimize these impacts.
Can Headphones Cause Brain Damage?
One of the most common questions people ask is whether headphone use can cause brain damage. Research has shown that prolonged exposure to loud sounds can indeed alter brain function, though it often requires continuous listening at unsafe volumes over time. Although there isn’t conclusive evidence linking headphone use directly to catastrophic brain damage, there are legitimate concerns about cognitive function deterioration as a result of constant auditory stress.
Tinnitus: A Common Headphone Side Effect
Tinnitus, the ringing or buzzing in the ears, is one of the most common side effects of prolonged headphone use. This occurs when the hair cells in the inner ear are damaged from constant exposure to loud sounds, causing them to send faulty signals to the brain. The result is often a persistent ringing sound that can range from mildly annoying to severely disruptive. Taking proper precautions with headphone volume and listening duration can help prevent tinnitus.
Effects on Sleep and Mental Wellbeing
You might not know this, but using headphones excessively—especially before bed—can disturb your sleep. Listening to music or podcasts late into the night can alter your circadian rhythm, affecting both the quality and quantity of your sleep. Moreover, overuse can lead to increased stress, anxiety, and even a dip in mood and concentration levels. Your brain needs recovery time, and overexposing it to stimuli like headphone use can interfere with your mental wellbeing.
Psychosocial Impact of Excessive Headphone Use
Spending too much time wearing headphones can also isolate you from your surroundings, causing a decrease in social interaction. This psychological aspect of headphone overuse might not seem obvious, but it can seriously impact your social connections and your mood. People who use headphones excessively may also find it harder to focus, as they’re constantly tuning out the world, which could cause heightened levels of stress or disengagement.
Protecting Your Brain While Using Headphones
Fortunately, there are practical steps you can take to protect both your hearing and your brain. Following the 60/60 rule (listening at no more than 60% of maximum volume for no longer than 60 minutes at a time) can greatly minimize risks. It’s also important to rest your ears periodically to avoid prolonged exposure to sound. Additionally, consider using noise-canceling headphones, which allow you to enjoy clear sound without having to turn the volume up too high.
What Research Shows About Headphones and Brain Impact
Recent research into the effects of headphones on the brain reveals that excessive use could lead to cognitive declines, particularly when high volumes are involved. Several studies suggest that listening to music at a high volume through headphones disrupts the neural pathways, which could eventually lead to changes in the structure of the brain related to memory and auditory processing. The findings urge users to moderate their listening habits to avoid long-term repercussions.
Technological Innovations to Prevent Negative Effects
Luckily, technology is stepping in to mitigate some of these dangers. Innovations such as noise-canceling headphones not only block out background sounds, allowing for clearer music at lower volumes, but they also prevent hearing strain. Additionally, newer models come with features that warn users when their listening volume exceeds safe limits.
When Should You Stop Using Headphones?
It’s important to be mindful of how much you’re using your headphones. If you experience signs such as ear pain, persistent ringing, or headaches, it may be time to take a break. Another indicator to watch for is an increasing inability to concentrate after long listening sessions, which is often a signal that your brain is being overstimulated.
Conclusion
Headphones have become a staple in modern life, providing comfort and entertainment at our fingertips. However, like many things, they come with their own set of risks to brain and ear health. Being aware of these effects—and taking appropriate precautions like limiting volume levels and use time—can help mitigate potential harm. Remember to prioritize your long-term health by enjoying safe listening habits.
FAQs
1. Can using headphones too much harm your brain? Yes, overuse of headphones, especially at high volumes, can potentially affect cognitive function and auditory health.
2. What is tinnitus, and how does it relate to headphone use? Tinnitus is a ringing sensation in the ears that can occur from prolonged exposure to loud noises, such as those from headphones.
3. Can I use headphones safely? Yes! Following safe listening practices, like limiting volume and taking regular breaks, can help prevent harm to your brain and ears.
4. Are noise-canceling headphones better for your brain? Yes, they allow you to listen at lower volumes while still enjoying good sound quality, which can reduce strain on your ears and brain.
5. What’s the best type of headphones for brain health? Over-ear headphones tend to offer the most comfortable fit and best sound isolation, which can help you listen safely without increasing the volume excessively.